Objective
- To find the pH of the given samples of solutions using pH paper
Materials required:
- Test solutions of samples (a) a dilute acid; (b) a dilute base; (c) 1 gm salt in 10 mL distilled water; (d) soil water extract and (e) a fruit juice
- Five test tubes
- Test tube stand
- pH papers
Procedure:
- Put the samples in separate test tubes. Mark each test tube
- Take a drop of sample in a dropper from each test tube one by one, and put on the Ph Paper
- Observe the changes in the ph Paper
Findings:
Conclusions:
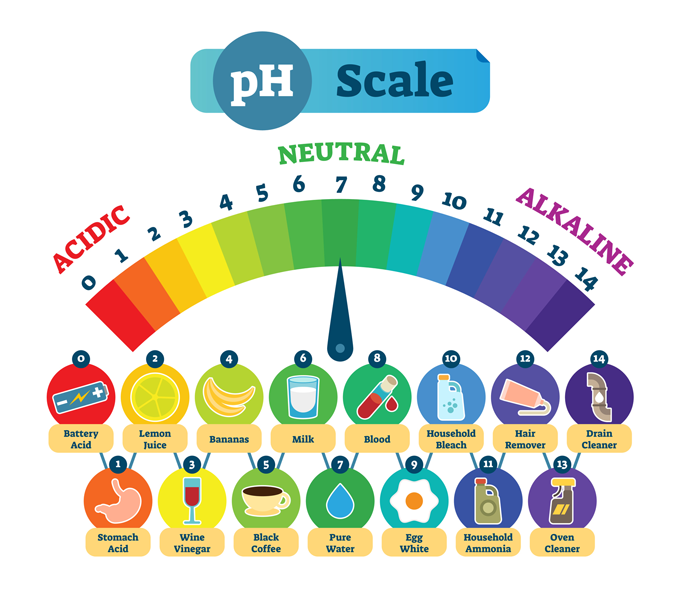
As pH depends upon H+ concentration and in an aqueous solution H+ and OH– ion concentrations are correlated, therefore, every acidic and basic solution shows different colour at different pH.
Theory:
- The pH is the measure of the acidic (or basic) power of a solution. It is a scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. The pH scale varies from 0 to 14. At 25 °C (298 K), a neutral solution has pH equal to 7. A value less than 7 on the pH scale represents an acidic solution whereas pH value more than 7 represents basic solution.

